Are you interested in finding out the best marketing buzzwords for a resume?
Do you need advice for buzzwords in a marketing interview?
Do you want to sound like you know your subject matter when talking with your colleagues?
As we will see, buzzwords have a lot of unconventional uses.
Table of Contents
Buzzwords Definition
A buzzword is defined as a word or phrase that appears authoritative or technical. It sounds in “vogue” in a particular profession, a field of study, culture, etc.
The speaker may not be an expert, but the usage of buzzwords gives a grand impression of them making them sound like an expert. So, we can, sometimes, call them ‘smart business words’.
Why are marketing buzzwords important?
Many professionals seek out advice for marketing buzzwords when looking for a job. They can make a great first impression by using buzzwords in a sales or marketing interview. Including marketing buzzwords in a resume can also put them several notches above their competitors.
If you are seeking a job in the marketing industry, do not use buzzwords that are not applicable in your scenario. Avoid buzzwords that you don’t understand.
When talking to senior leaders in any industry, you may hear such words that you have never heard before. To the speakers, these are smart business words.
Conversely, the same words are often repeated so frequently that they become the most hated marketing buzzwords.
Some people attach a negative connotation to “buzzwords”. For them, most marketing industry buzzwords are nothing but meaningless conversation fillers.
Buzzwords in a digital agency’s marketing copy also have the same effect. It helps them connect with their potential clients, who are often C-level executives.
In this article, we will list and explain the meaning of some of the most common buzzwords from marketing, sales, and customer service.
What are some latest marketing buzzwords in 2020
Exposure to elementary digital marketing terminology will be helpful but not essential in exploring buzzwords used in marketing for different subcategories.
Advertising Buzzwords
If you are going to an interview in an advertising company or if you want to avoid overused words, here is a curated list of advertising buzzwords:
Contextual marketing
Imagine you saw a local ad for Christmas Sweaters on sale. The same ad will convert better if it aired on December 20 than if it aired on November 20.
Ever wondered – why this happens?
As we get closer to Christmas, the deadline gets closer. In other words, the “context” of Christmas intensifies in our minds as we get closer to December 25. So, an ad airing on December 20 can capitalize on this context and sell more than an ad aired on November 20.
Extrapolate this idea and you get contextual marketing. It’s the central tenet of all successful inbound marketing. It simply means serving ads to those people who want to buy similar products.
The simplest example of this is ads on Google SERP (Search Engine Results Page). You see ads based on the keywords you searched for.
A cookie can also live on the user’s computer to track their activity. the ad service provider then reads this cookie to recreate a behavioral profile (i.e. “context”). This becomes the context to show personalized ads specific to the user. This is contextual advertising or contextual marketing.
The goal here is to not show irrelevant ads and thus make ads seem natural.
Micro-moments
The Micro-Moments model was first proposed by Google in 2015. It prescribes 4 distinct types of highly-focused, intent-filled interactions called “moments”. During these moments, consumers want to instantly fulfill their needs.
While smartphones are not specified as the device of choice, this model addresses needs in the mobile advertising realm.
Depending on the type of visitor need they represent, Micro-Moments have 4 types:
- I-want-to-know moments: When the visitor wants to know something instantly but may not buy something
- I-want-to-go moments: When the visitor wants to locate a business with an intent to visit them or buy from them.
- I-want-to-do moments: When the visitor wants to complete a task or is doing something new
- I-want-to-buy moments: When the visitor is ready to buy but needs help in deciding what to buy or how to buy
If brands can display their ads during these micro-moments, they have a high chance of becoming their favorite. Hence, these moments become “preference-shaping”.

Attribution models
Attribution models help present a holistic picture of conversion events. They help advertisers understand which channels are attracting the most customers efficiently.
Attribution models are rules that help decide the percentage of contribution of each touchpoint to the final sale. Advertisers can then measure the impact of their investment and optimize their marketing budgets.
Attribution models can be simple – first-click, last-click, or linear attributions. They can also be complex:
- Time decay (touchpoint closer to the sale time gets more credit)
- U-shaped (first and last touchpoint share equal credit, all other touchpoints share equal credit)
- Algorithmic or data-driven attribution (dynamic attribution, based on machine learning algorithms)
It’s important to understand that customers can use a wide variety of touchpoints. Attribution modeling is a complex process where the “holy grail result” is far from reachable.
Media Agnostic
Often, brands hire agencies with the sole purpose of creating a TV ad. But a media-agnostic hiring strategy creates a message that reaches a brand’s audience where they may find it – a newspaper ad, a Snapchat ad, or a TV ad.
Programmatic Buying
It’s just another word for automated buying of advertising spots. .This could be through a brand’s automated programs that run pre-set algorithms. Brands may also directly interact with the publisher’s software to buy their preferred ad spots.
Rich Media
Rich media includes types of media where the original ad expands to take up more space. Viewers to interact with it through a video, a mini-game, a quiz, and so on. When rich media are used, advertisers can create interactive and immersive advertising experiences.
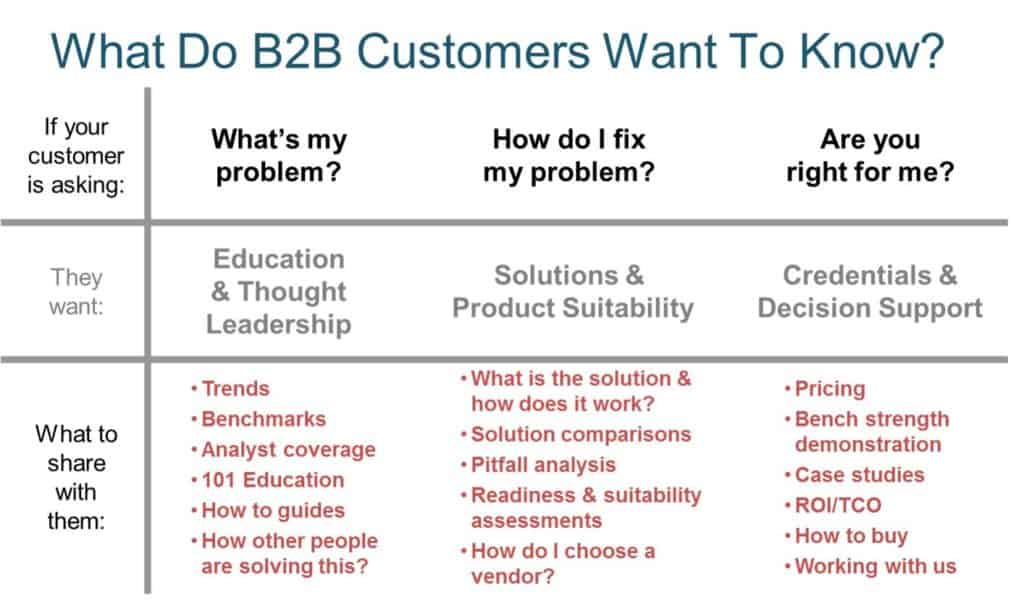
B2B Marketing Buzzwords
The image below classifies the problems and a path to solving them for B2B marketers.
[Source: Wikimedia Commons]
It’s easy to misunderstand and use these B2B marketing buzzwords. This section contains a list of marketing buzzwords for every B2B marketer to avoid. B2B marketing aspirants can also include them in their resume).
[Source: Tara Hunt / Flickr]
So, here is a list of terms that a brand marketer must know (or avoid)
Brand Identity
A brand’s identity is the sum of its “visual look” and the “core message” that the customer or prospect receives when they consume their product or service.
Typically this includes:
- Name
- Tagline
- Typography
- Color
- Patterns
Brand marketing helps create an identity by communicating brand identity to consumers.
The goal of brand marketing is to establish trust, credibility, and help form an emotional bond with the consumer.
Branding Strategy
Branding strategy is a long-term plan to conduct brand marketing activities to achieve various goals such as:
- customer-reach goals
- sales goals
- other brand identity-based goals.
Creating a branding strategy may seem like a waste of time. But it is crucial to developing a plan for predictable long-term growth and refined communication.
Brand Equity
Brand’s equity is the financial, emotional, and other forms of brand value that are expressed as:
- Market share
- Revenue
- Strategic benefits that the brand offers to its consumers
- Anything else in the answer to the question “What is your brand worth?”
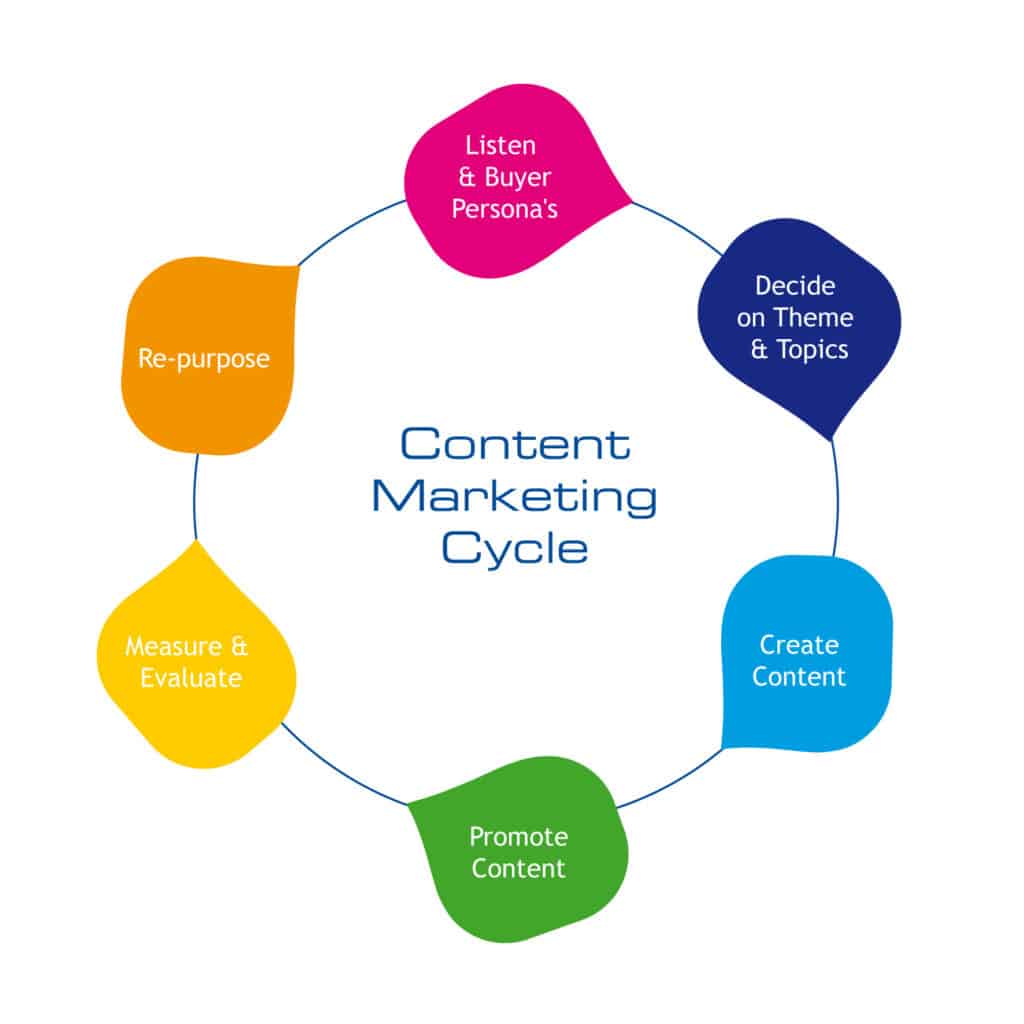
Content Marketing Buzzwords
The image below describes a basic framework of content marketing activities:
[Source: Wikimedia Commons]
This section will help you get acquainted with some common terms that every content marketer must be aware of.
Avoid or embracing them is their choice.
EVERGREEN CONTENT
Evergreen content stays popular (i.e. “fresh”) long after publishing. It is the type of content that retains relevance over a long period (ideally “always”). As a result, as long as evergreen content pieces rank well, they draw in a lot of traffic. But this traffic may not be consistent.
Some examples of evergreen content include:
- How to Lose Weight Without Dieting
- How to Fry an Egg (Last Updated: April 9, 2009)
Note that “evergreen content” doesn’t mean “always popular content”. It can also mean “seasonally popular content” such as those related to Thanksgiving, Halloween, and Christmas.
Investing in evergreen content opens up a Pandora’s Box of conversion opportunities. This makes it a very powerful content marketing strategy. From a single evergreen content, you could link to more “focused” topics to distribute the traffic throughout your website. You could also sell products or share lead magnets on this single piece of content.
Micro/Macro conversions
Conversions can be further divided into two subtypes: Macro Conversions and Micro Conversions.
Macro conversions are the main (revenue-generating) goals of a website. For example, buying a product, creating a booking, or donating.
We want these macro conversions as many times as possible. But we all know, consumers are too smart to empty their pockets on the first visit. So, the frequency of macro conversions is lower than micro conversions.
Growth Hacking
Growth Hackers are content marketers who commit to growth as their “north star“. Every campaign they run and every strategy they execute helps the company grow. They have highly-focused growth-oriented thinking.
These skills help early-stage startups achieve quick, transformative growth spurts on low budgets.
Growth Hacking uses smarter alternatives such as:
- precisely-targeted ads
- brand building through social media
- viral marketing.
These measures build upon existing growth techniques to overcome the challenges of small businesses.
“Instead of bludgeoning the public with ads or dominating the front page of a newspaper to drive awareness, they [Growth Hackers] use a scalpel, precise, and targeted to a specific audience.” – Ryan Holiday, Writer, Media Strategist, CEO @ Brass Check.”
Dave McClure’s “AARRR Framework” (also known as the Pirate Funnel) gives a really simple way to start hacking the growth of your own business.”
If you want to read more, Melanie Balke has a great post about it on her Medium blog. Ward van Gasteren also has a nifty guide to the Pirate Funnel on his website.
Low-hanging fruit
Low-hanging fruit is an easy-to-achieve goal or an easy-to-implement technique. Like a low hanging fruit, they do not need much effort to achieve.
This term is often used to classify keywords with high volume and low difficulty score. If the marketer created content around such keywords, they would be easy to rank.
Any quick and easy change that produces (relatively) instant results is also low-hanging fruit.
Digital Marketing Buzzwords
Digital marketing is as old as the internet itself. Ever since companies started using the internet to market themselves, several terms have arisen out of the collective consciousness of digital marketers worldwide.
While some may argue that these are overused, others would think of them as important to learn to create the influence.
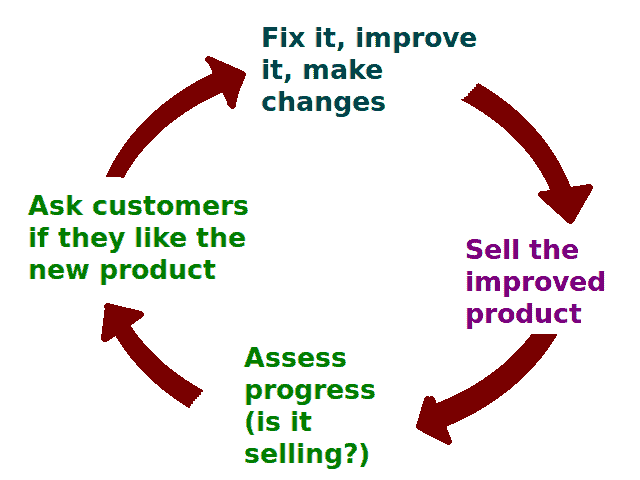
The image below describes how to create a digital marketing strategy.
To buy something, the user will visit one or more product pages. When they decide to buy, they first move the item to the cart. Finally, it culminates in payment confirmation. All these are milestones in the buying process – also called Micro Conversions.
Actions such as viewing product pages or adding an item to the wishlist (or the comparison tool) are not a step toward a sale. They are a type of micro conversion also called the secondary action.
[Source: Wikimedia Commons]
UTM parameters
UTM stands for Urchin Tracking Module. Urchin was the predecessor of Google Analytics.
UTM parameters are custom name/value pairs appended at the end of any URL. Through these parameters, you can supply extra (string) data for use in source tracking. Google Analytics uses these parameters to measure the performance of different traffic sources.
You can also code your website to provide source-specific user experience with UTM parameters.
For example, the URL example.com/homepage with UTM parameters “source” and “campaign” attached to it may look like this:
https://www.example.com/homepage?utm_source=instagram&utm_campaign=sponsored
The value of the “source” parameter is “instagram” and that of the “campaign” parameter is “sponsored”.
The mandatory construction rules for UTM parameters are as follows:
- The names of both parameters must follow the string “utm_”.
- The parameters follow to the original URL with a “?” sign
- The parameters follow each other with a “&” sign.
Path length
Google Analytics provides a wide variety of conversion reports. To track multi-touchpoint conversions, you would use the Multi-Channel Funnels option. Path Length is a type of conversion report for multi-channel funnels in Google Analytics.
The Path Length report will track the number of conversions v/s the number of user interactions for each path length. It helps understand an optimal path length for conversions on your website.
For example, if most users saw your ad 3 times, then the number of interactions (I.e. path length) is 3. If the revenue drops significantly for greater than a path length, use frequency caps to limit the path length. Frequency caps limit the most number of times a user will see your ad.
Psychographic Segmentation
This technique focuses on answering questions about the target audience group that connects you to their heart and soul. It goes beyond the question of “how they will respond” to help you understand “why they will respond this way”.
Some psychographic factors used for such segmentation include:
- Values
- Motivations
- Priorities
- Lifestyles
- Personality Traits
These factors help form an emotional and personal connection with the users. The net effect is stronger buyer personas and better contextual marketing strategies.
Data-driven
It refers to the decision-making strategy in companies that use modern digital marketing tools. If every decision is based on concrete data, the company does not have to play a guessing game or use someone else’s strategies to make decisions.
A commitment to data allows a company to make its own decisions based on provable insights. It can be confident of its outcomes.
Customer Journey
Marketers define the customer journey as a series of steps that a typical potential customer can take. It starts from the first point of contact to their first sale and beyond. The goal is to figure out what are those steps and how the potential customer transitions from each one to the next.
Omni-channel
It’s a way to offer shopping experiences with seamless transitions across different shopping channels.
For example, a virtual discount voucher that the customer can use in physical stores or on the online store of the brand.
Omnichannel support is also an emerging subcategory. The customer can raise a ticket on one channel (say, a Twitter DM) and continues the conversations across all channels (say, email) seamlessly.
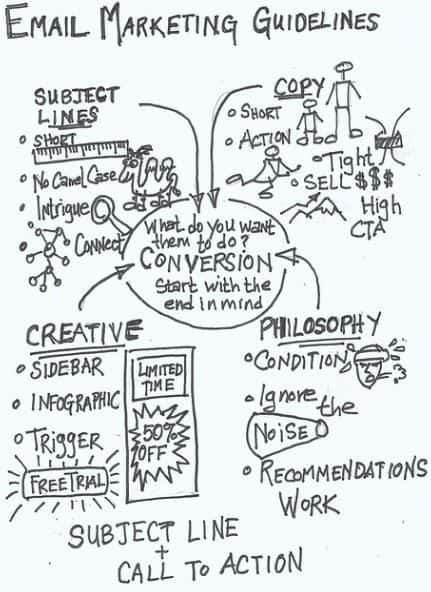
Email Marketing Buzzwords
The image below describes the most important terms in Email Marketing and how they relate to each other.
[Source: Bill Rice / Flickr]
Email marketing blows all the other marketing channels out of the water; it delivers the highest ROI ($38 over every $1 spend).
The main challenges with email marketing are: how to get the users to open and click-through the emails and how to do it efficiently.
The three buzzwords in this section will help you achieve that goal.
Personalization
By personalizing emails, marketers can create content to fit each customer’s behavior profile on the company’s website.
It started with marketers being able to add the receiver’s first and last names in the subject line and the content. Now the email automation technology has advanced. Marketers can now personalize email content by using specific tags given to user groups.
Segmentation
No marketing content will be useful if it’s not relevant. By segmenting the email list, a company can address each group of its users separately and give them all equal attention.
Segments can be based on:
- Geographical location
- Demographic data
- Website activity
- Prior purchase data
And so on!
Automation
By automating triggered emails, you can respond to user activity and behavior change instantly.
For example, as soon as a customer completes an order on your website, the system can send an order confirmation email. This email will contain suggestions for other products that the customer might want to buy, besides a product invoice.
The timing of this email enhances the relevance of the email messages. This is the principle behind all triggered emails.
With modern marketing automation systems, you can set up email workflows to send an email in response to a specific condition/event.
Experiential Marketing Buzzwords
Experiential marketing attempts to create holistic experiences for potential customers. It does not rely purely on textual ads.
With experiential marketing, customers can immerse themselves and engage with the brand in as many ways as possible. These interactions are within the context of a large event or many small events stacked together.
The ultimate goal here is to let the customers form an emotional bond with the brand through memorable experiences. This leads to increased brand loyalty and higher customer lifetime value (CLV).
Let’s learn some buzzwords to understand this type of marketing strategy better.
Immersive
Technologies like Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (VR) or a mixture of both help make the experience memorable. “Immersive” is an adjective given to such an experience.
For example, a VR app that gives potential home buyers a tour of the space on a VR device. One can also test various home or building designs through VR without creating prototypes.
WOW! Moments
The experience of a brand is a result of many small moments called WOW moments.
To create these moments, one must move toward an “experience-based terminology”. So, the “smallest viable product” gets replaced by the “smallest acceptable experience”.
Iteration only happens when the event gets a second run. That means the planning and execution of the first run must be flawless. Otherwise, you could get failures as large as the Fyre Festival.
Multisensory Marketing
Brand experience can become effective and memorable when it combines many senses. It doesn’t have to focus only on visual experiences.
For example, a Dunkin’ Donuts campaign in South Korea used auditory and olfactory senses (smell) to increase visits by 16% and sales by 29%.
The trick was to play the company jingle as an audio advertisement on the municipal buses as they neared Dunkin’ Donuts store locations. Along with the jingle, an atomizer device released the aroma of coffee to engage the smell senses of the passengers.
Using more than one sense for marketing can have its flip side too.
Healthcare Marketing Buzzwords
When reading marketing content for the healthcare industry, you may notice common words/phrases. For an industry insider, these terms are overused cliches.
For someone reading them for the first time, these can be daunting.
So if you want to make your resume attractive or make an impression in your next interview, here is a list of healthcare marketing buzzwords you can use:
Close to home
This phrase conveys a high quality of care available locally to patients, without traveling to the nearest city or a large care facility.
But the term itself, despite being simple to understand, doesn’t communicate much.
Marcomm professionals must find different ways to explain what close to home means and what impact it has on the brand’s services.
Caring and compassionate
These adjectives are also quite simple to understand, but too often they are treated as just words.
The truth is – we expect care and compassion from every healthcare professional; it’s the norm. But this may not be true for healthcare companies, which often have the opposite image.
The solution, again, is simple: SHOW, DON’T TELL.
How can you communicate the level of care and compassion of the service provider without using those exact words?
Cutting edge/leading edge/state-of-the-art/world-class
These are common terms to use a highly advanced piece of technology. Unfortunately, these are also overused.
Once again, the show, don’t tell principle comes handy.
Instead of using these phrases, you may use words that help prove the benefits of the new technology.
Influencer Marketing Buzzwords
Marketing through influencers is quickly becoming the norm, especially in the B2C industry. This makes learning the nuances of this marketing strategy imperative to understand. Not only does it help understand the brief from senior management but it also helps to take stock of your influencer marketing strategy.
To avoid any potential confusion, let’s look at some common influencer marketing buzzwords.
Opt-in Influencer Programs
To conduct an influencer marketing campaign, you can run an opt-in program and invite influencers to sign up. They can post content promoting your brand. It minimizes the role of the brand in the engagement and opens up the content creation to the influencers.
There is hardly any control over the quality and hence opt-in influencer programs are generally avoided.
Ambassador Programs
Within Ambassador programs, influencers don the role of Brand Ambassadors. They post many types of posts at different times of the year for year-round engagement.
Your brand must work with only those influencers that have a high impact on your target audience.
Equivalent media value
This is a metric that shows how many units of a type of media will give us the same number of impressions for another preferred media type.
It is often used to compare different advertising media types.
Targeted amplification
We can combine content with high potential for conversion with influencers having a high impact on a brand’s target audience. This allows us to amplify performance beyond traditional content distribution through influencers.
Ad relevance score
An ad’s relevance score increases when an influencer share a brand’s post and the post has more engagement. This is because more people can relate to it.
But people may also show an adverse reaction to the ad through low engagement numbers, negative comments, or a high ad reporting rate. This reduces the ad’s relevance score.
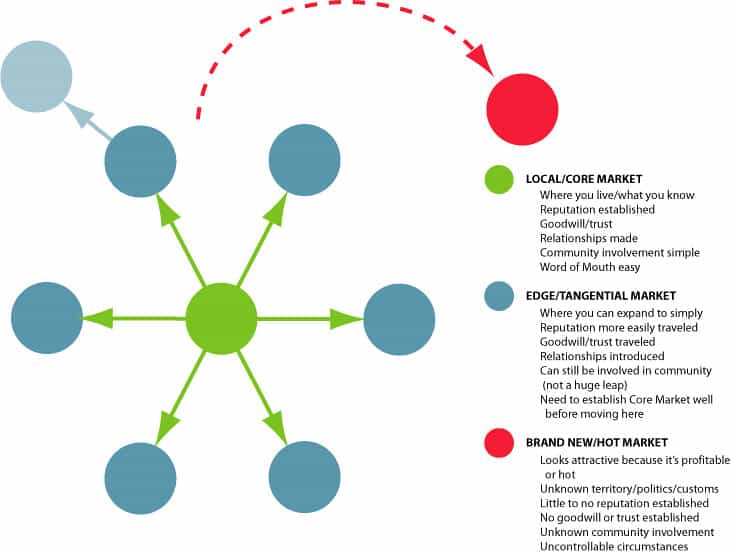
Local Marketing Buzzwords
How can a small store make the best use of digital marketing avenues to build a brand and get more sales?
By marketing within their local neighborhood.
The following avenues can be very effective in utilizing local marketing bandwidth:
- The local event and/or team sponsorship
- advertisements on local news channels
- advertisements in local newspapers
The image below offers a fair idea of how you can shape your local marketing strategy.
[Source: Wikimedia Commons]
But if you are new to local marketing, certain key terms are important to know and understand.
Mental maps
Residents know their locality and all the important businesses in their vicinity.
They note their favorite restaurants and stores within their locality to avoid going far for social activities. These places often experience a lot of repeat business.
One of the core objectives of local marketing is for the store/business to make its way into the mental maps of its regular customers.
Localization
This is a very important step for all stores engaging in local marketing.
You can adapt your content language into a language that local patrons understand. This enables an easy connection with them and you give them a reason to share your business with their friends.
Localization of your website (and in general, marketing communication) is not essential.
If yours is a semi-urban or an urban locality, great marketing content in plain English should be enough. But with localization, you can take up your sales and brand recall to a whole new level. It removes any cognitive barrier that may come in reading English content.
Localization may be mandatory if your audience tends to not understand English as much as you do.
The only way to decide on localization is by doing some Split testing. If the return on localized communication exceeds English content, the test has succeeded.
Word-of-mouth Marketing
It’s the medium by which brand perception spreads among residents. You can leverage the power of word-of-mouth marketing by creating delightful in-store experiences.
Tactics such as loyalty programs for loyal patrons help develop a community of local influencers. They can help drive your store’s word-of-mouth marketing.
Restaurant Marketing Buzzwords
The image below outlines a standard procedure by which restaurants can connect with their visitors and gather feedback.
[Source: Wikimedia Commons]
Consumers are becoming more aware of where the food comes from and how it is produced. They place unique demands on the food and restaurant market.
As a direct result of that, marketing communicators have had to align their vocabulary to cater to a diverse audience. The buzzwords introduced into the restaurant marketing industry can become a bit tricky to understand for non-consumers of such unique products.
This section introduces some of these words that have gone on to become buzzwords.
Farm to Table
“Farm-to-table” means it has been directly sourced from a local producer without any middlemen. The “farm” here could be any type of producer such as a winery, brewery, ranch, fishery, etc.
The idea is to eliminate “factory farming” corporations that take livelihood away from local producers.
To the producer, a ‘farm-to-table’ product gives a larger share of the profits. For consumers, it assures fresh, unprocessed food, and enrichment of their local communities.
Alternate names for this social movement are ‘farm-to-fork’ or ‘locally sourced’. Another variation is ‘farm-to-school’, where the food is bought in large quantities to serve in school and college cafeterias, often sourced through the best soil program initiatives to ensure the highest quality and sustainability in farming practices.
Grass-fed
‘Grass-fed’ is an adjective given to a special type of beef when the cows are fed with grass (instead of grain, soy, or other supplements). The meat from grass-fed cows has less fat (hence fewer calories) and higher levels of Omega-3 fatty acids which open up many health benefits. Hence, grass-fed is considered healthier than grain-fed beef.
Not all cows may be fed with grass all the time; often ranchers feed them with a mixture of grain, soy, and grass. If cows are fed with only grass until they reach the slaughterhouse, their meat is ‘grass-finished’ (or 100% grass-fed).
If cows can roam in pastures to consume the grass (instead of eating grass in closed enclosures inside sheds), their beef is ‘pasture-raised’.
Sustainable farming
The practice of agriculture has a large environmental footprint. It has many negative effects on the prevailing production conditions:
- reduces soil productivity for future generations, making them unsustainable.
- contributes to climate change and causes water scarcity and land degradation
- causes deforestation
Sustainable farming practices aim to replace traditional agricultural practices with sustainable food production systems. To goal is to reduce/eliminate these side effects to preserve the sustainability of farming conditions for future generations.
Some of the sustainable agriculture practices are as follows:
- Reduced or eliminate tillage to prevent soil degradation
- Cover crop plantation that makes the most out of less productive soil seasons.
- Crop rotation to make use of diversity to improve soil health
Social Media Marketing Buzzwords
When businesses rely on social media to market their products/services, their team embraces any new word that comes their way. The danger here is, of course, when people start using these buzzwords without really understanding what they mean.
So, this section explores such buzzwords that social media marketers must know and use correctly.
Impressions
For a social media advertisement, ‘impressions’ are the number of people who see the ad. Another name for it is ‘actual reach’. It is different from (and lower than) potential reach which we see in Ads Management systems before publishing the ad.
Engagement is a combination of the number of likes, comments, and shares. It is cumulatively a smaller number than the number of impressions.
Dark posts
Advertisements published on Facebook can come from two sources.
If an existing high engagement post on the company’s Facebook page is ‘boosted’ to expose to a wider audience, such an ad is called a ‘Sponsored Post’.
If the company creates a brand new ad directly in Facebook Ads Manager, those are called ‘Dark posts’ because they are not visible publicly.
Retargeting
It’s the practice of showing social media ads to those people who have already interacted with your brand on its website.
If you have the Facebook Pixel code installed on your website, you can use it to source audiences within the Facebook Ads Manager. Alternatively, you can insert your entire (or segmented) email list to define your audiences.
For example, someone sees a few t-shirts on your eCommerce store and leaves without buying them. You can remind them about the t-shirts by putting an ad about them on their timeline.
Social Media KPI
Certain KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are used to set goals for social media performance. The progress (or regression) of these metrics defines the performance of social media executives.
Some examples include:
“Interactions per post” which includes all types of reactions, comments, and shares.
The number of likes on the company page.
Impress them with Buzzwords for all purposes
The words we saw in this article are real-world buzzwords. They are simple, they’re meaningful, and they’re useful in various scenarios.
They can help add weight to your conversation without making you sound like a know-it-all.
They can also help add the much needed “X-factor” to your resume or start-up pitch decks.
Which buzzword is your favorite from these lists? Have you heard a buzzword that made you cringe or you found it so impressive that you just had to share?