Broad email marketing doesn’t perform as well as personalized, tailored campaigns. The key to customizing your email campaigns is understanding your audience, and that begins with list segmentation.
You can divide your audience by a thousand criteria, including basic and more advanced points.
This guide is chock full of advanced segmentation strategies to help you understand and connect with your eCommerce email audience for better engagement, more conversions, and higher open and click-through rates.
Table of Contents
eCommerce Email Segmentation Strategies for Demographics
1. Age
Beginning with demographics, age is one of the simplest qualifiers you can use when segmenting your customer data.
The age of your audience influences the products and services they’re interested in, the messages they’re most receptive to, the communication methods you should use in your campaign, and the amount of money you can reasonably expect them to spend.
2. Birthday
Birthday and age go hand-in-hand, but they’re separate segmentation criteria. You can use a customer’s birthday to personalize emails, but it goes beyond that.
For example, you can tie seasonal offers to a customer’s birthday, such as a winter vacation offer for those with winter birthdays.
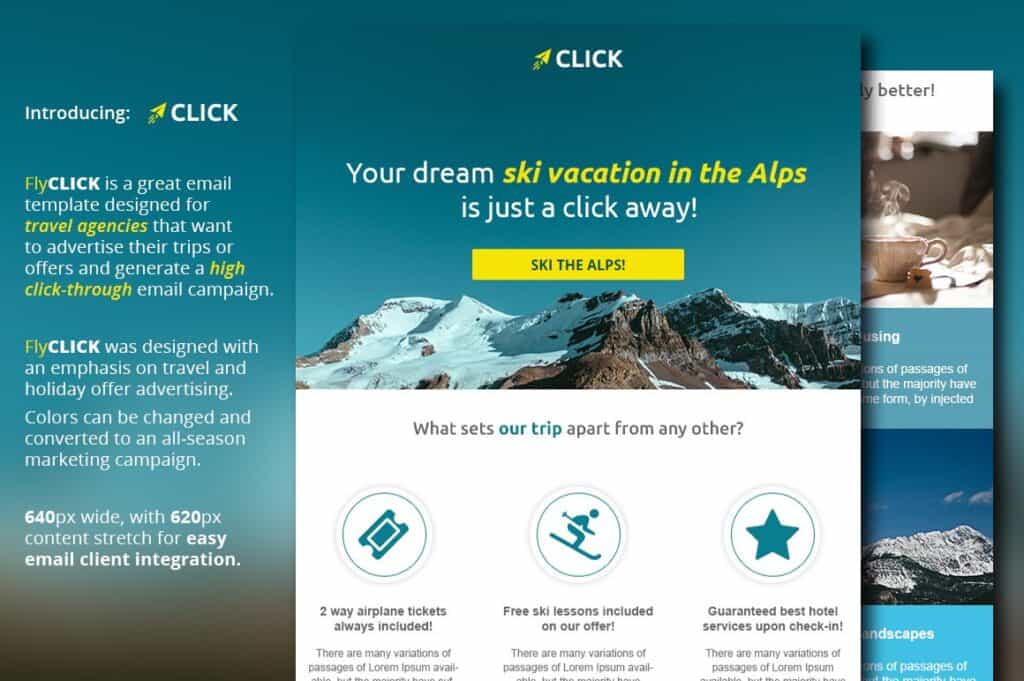
Adding a special discount code incentivizes a purchase.
3. Gender
One of the simplest criteria for eCommerce email audience segmentation is gender. You’ll rarely use gender alone when crafting messages for your email list, as it’s too broad a criterion, but in conjunction with other demographics, geographics, and psychographics, it helps paint a clearer picture of your customers.
4. Occupation
What do your customers do for a living? Knowing your audience’s respective occupations also tells you what kinds of products and services they’re interested in (or may be interested in), what kind of pain points they may have, and how much money they can afford to spend.
5. Business Industry
You can dig a lot deeper than a customer’s occupation. For example, what industry do they belong to?
An accountant is part of the finance industry while a pizza parlor employee is part of the hospitality industry. One’s industry paints a broader picture of your audience’s occupational pain points and earning potential.
6. Business Type
You should also know the business type of your audience. Industry and type are different criteria that serve to provide even more details as you build customer profiles and strengthen your segmentation strategy.
7. Seniority Level
Many occupations have seniority levels. To continue the example from earlier, an entry-level accountant is not on the same professional level as a senior accountant.
The latter has far many more years of experience, so they’ll have different challenges you must address with your products and services. One’s seniority level might also mean they’re readier to make a purchasing decision.
8. Income
This is by far one of the most important demographics, possibly the most important, as understanding your eCommerce audience’s income tells you what they can afford to spend on your products and services.
You can then tailor your eCommerce email messages appropriately, recommending items within their price range. This targeted segmentation strategy avoids offending your audience by recommending them lavish products they can’t afford and should lead to more sales.
9. Marital Status
Are your leads and customers married? This is handy information to have, as a single person’s needs vary from those of someone who’s tied the knot. They’re usually more family-minded, influencing the types of messages they’re receptive to.
10. Number of Children
You must also know the number of children your customers have, if any. This information further specifies which types of products and services to promote through your email marketing campaigns.
For instance, let’s say you’re a furniture company. Your unmarried, childless customers will have no interest in the brand-new baby furniture you’re promoting. Your married audience might be interested, while your customers with families should certainly be interested.
You could instead promote your new bedroom set to the customer groups without kids to generate sales from your entire audience base.
Read also: A Comprehensive Guide To eCommerce Email Segmentation
11. Nationality
You should also learn your audience’s respective nationalities, such as Russian, Canadian, Indian, or American. This information will help you personalize your email communications. Just keep in mind that one’s nationality is not necessarily tied to their geographical area.
12. Race
Understanding your audience’s race paints a clearer picture of who they are. Examples of race include Pacific Islander, Native American, European American, or African American.
13. Religion
A person’s religion can be a deeply personal thing, so your audience might not always feel comfortable sharing this information. However, if they are, it’s one more detail you can file away on their customer profile.
Knowing a customer’s religion allows you to send emails on pertinent religious holidays and observances. However, lean on this demographic sparingly.
14. Education Level
How much education does your audience have? Are they GED holders, or do they have an associate’s degree? How many have a bachelor’s degree versus a master’s degree? What about specialized degrees and titles?
Understanding educational information is helpful in lending your emails more personalization.
15. Skill Level
The last demographic to add to your list when segmenting your audience is skill level.
What kind of skills does your audience have, and how good are they? A person is undoubtedly interested in the subject they dedicate a lot of their time to mastering. That can help you with product and service recommendations.
Read also: eCommerce Email Marketing UTM Parameters [101]
eCommerce Email Segmentation Strategies for Geographics
16. Country
Moving on to geographics now, the next segmenting criterion is one’s country. The world is a huge place, so where do your customers reside?
This information is only a starting point, as segmenting your email list based on country alone produces large, broad groups, and specificity is always better.
17. State
The next geographic criteria you can use for your eCommerce email list segmentation is the state. For example, focusing on customers in the United States, how many live in Florida versus New York? Dividing your audience by these specific geographics will shrink each group.
18. City/Town
We recommend going more specific still, such as dividing your audience by the city or town they live in. Some cities and towns, such as Toronto or Chicago, are large, while others will be smaller and more obscure, so your audience size will vary.
19. Neighborhood/Borough
You can even divide your audience geographically by neighborhood or borough if you want ultra-specific niches. We’d recommend this kind of tailored geographic data for local businesses that want to connect with their audiences, such as real estate companies.
20. Weather
Weather influences our daily lives, yet patterns of precipitation and sunshine can vary wildly all over the world. Even knowing when certain customers experience winter weather can help you send emails catered to them.

Take a look at the wintry email from retailer West Elm. It wouldn’t make sense to send this email to people in South America in January, as winter happens in June for them. However, this would be a good email to send your US audience, as winter is in full swing by January.
Read also: eCommerce Email Marketing Simplified: 15 Examples + Tips
eCommerce Email Segmentation Strategies for Psychographics or Customer Behavior
21. VIP Status
Next, let’s look at psychographics and customer behavior segmentation strategies, starting with VIP status.

The customers you consider VIPs have been with your business for a while. They’re highly engaged with your content, purchase products and services regularly, and are incredibly loyal. They’re likeliest to engage with your new services and products, so keep them in their own category.
22. Webinar Attendance
Who attended your latest webinar? Besides the thank-you emails you send, you should also create a drip campaign for this group to entice them to partake in the next webinar. You might offer them a special discount to drive their business.
23. Membership Expiration
If your business offers a membership service, separate your audience based on who’s just beginning their membership versus those midway through it and nearing the end of their service.
You can use email automation to send reminders throughout the membership so customers don’t miss their chance to renew for next year.

24. Purchase History
What kinds of purchases have your audience segments made? Do they buy one type of product or service from you, or are their purchases all over the place?
If they have rather predictable buying behavior, you can use their history to recommend products and services you know they should be interested in.
You can also use purchase history to cross-sell and upsell your audience, recommending related products based on what they’ve already purchased and own.
25. Event Attendance
Event attendance is part of an important email marketing segmentation strategy. Past event attendees should enter a specific email funnel designed to build their interest in the upcoming event, announce ticket sales, present early-bird offers, and upsell with VIP packages.
Your email marketing strategy will be completely different for prospective first-time attendees but equally as important.
26. Entry Point
A lead or customer entry point is how they interact with your business, whether from an opt-in form, a customer referral, an advertisement, a blog post, etc. Discovering how your audience finds you allows you to connect with them on a platform they already use.
27. Abandoned Cart Status
No business wants abandoned carts, but they are inevitable in some respects. The average cart abandonment rate is 70.19 percent, according to the Baymard Institute and its collection of nearly 50 studies on eCommerce shopping behaviors.
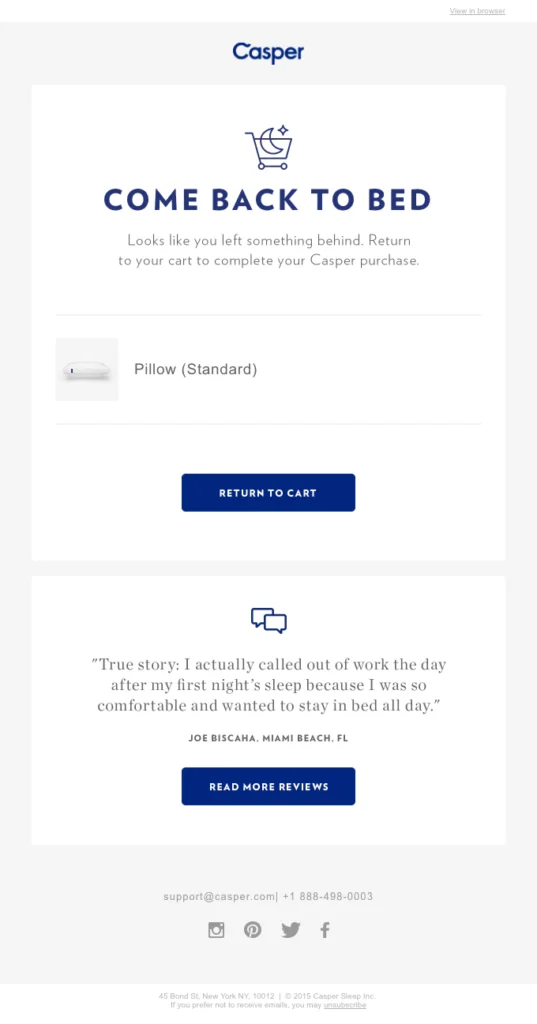
Determining which audience members abandon their carts allows you to send targeted emails, like the one seen above, encouraging a second look at a product. Adding a discount code can also inspire fewer abandoned carts.
28. Personal Interests
What kind of interests do your audience members have? These interests are likely outside of your business, which is fine. Knowing the hobbies and passions that kindle your customers’ fires puts you in an advantageous spot for suggesting related products and services under your brand umbrella.
29. Purchase Frequency
Segmenting your audience based on their purchasing frequency is another criterion to strongly consider.
You should send emails more often to those customers who don’t buy as much, reminding them of your stock, introducing new products and services, and issuing plenty of enticing discounts.
You should also send a steady stream of messages to your frequent buyers to encourage them to continue purchasing.
30. Website Visit Frequency
What about the leads and customers who visit your website? What kind of content do they spend the most time on? For example, if it’s blog content, you might incorporate more blogs into your email newsletters.
31. Time Between Purchases
How long do your customers wait to complete a purchase after completing an initial one? You should research the average time between purchases for the types of products or services you sell, then strive to match that time for your own goods.
You might even reduce the amount of time below the average, boosting your bottom line in the process.
32. Social Media Engagement Level
Engagement on social media might seem disconnected from email marketing, but we disagree. You can use social media to determine the kind of content your audience enjoys, then send them more of that in your email campaign.
You can also use email as a vehicle to increase social media followers and engagement.
33. Website Behavior
Besides the frequency of website visits and the pages most visited, what else do leads and customers do on your website?
How long do they spend on each page? How long do they spend on the website overall? Perhaps they know what they want, so they’re quickly on and off, or maybe they spend a lot of time reading your FAQs.
Segmenting your audience based on website behavior can help your small business turn those website visits into sales.
34. Sales Funnel Position
Here is one of the most basic but important email segmentation criteria, where your leads and customers are in the sales funnel.
Leads who have just entered the sales funnel should receive a different email cadence than long-term customers. They need more nurturing and engagement to move through the funnel and convert. You’ll send frequent emails.
Long-term customers don’t need nurturing, but you should still prioritize email engagement to keep them interested in your products and services.
35. Customer Lifetime Value
CLV, which is short for customer lifetime value, indicates a customer’s worth for their time as a customer. You can calculate CLV by multiplying the average lifespan of your customers and the average customer value.
Customers with a higher CLV should receive VIP-level emails that treat them well to keep them engaged and purchasing. You should also ramp up sales efforts with customers with a moderate CLV to realize more of their potential.
Read also: Finding the Best Customer Segmentation Software: A Detailed Analysis
36. Amount of Money Spent
How much have your customers spent on your small business? This is critical to gauge your CLV. Just as you should segment customers with a high CLV into a targeted email funnel, the same goes for your biggest spenders.
Lesser spenders should receive more frequent offers and discount codes to motivate them to start spending more.
37. Brick and Mortar Purchases
Does your startup have a brick-and-mortar store? You should know who goes on this email list based on your geographic data and tracking brick-and-mortar purchases.
It won’t be a large group, but they should receive offers for your store that customers who live further away do not.
38. Type of Purchases
Few email segmentation criteria are as helpful as the types of purchases a customer makes. You can use this information to inspire them to purchase more of the same or branch out into different areas of your products and services.
39. Most Recent Purchase
You can also split your audience based on their last purchase. This is yet another golden upsell or cross-sell opportunity depending on what the purchase is.
For instance, if a customer buys a laptop, you can recommend them a case, a charging cord, antivirus software, and a mouse.
There’s no need to send a separate email about these products when you can mention your offer in the order confirmation email.
40. Most Reviewed
Your marketing automation should also segment subscribers who leave the most reviews. These customers are likeliest to review your new products when they buy them.
Read also: Customer Segmentation Examples & How To Follow Them
41. Least Reviewed (Or Never Left a Review)
You should also set aside the group of customers who have yet to review your products and services and those who write sparse reviews. You might offer them a discount code for reviewing your products, or add them to a raffle or giveaway for their participation.
42. Survey Results
You should survey your audience several times per year to determine whether their geographics, demographics, and psychographics have changed and where they might fit into your ever-evolving audience groups.
Create a segment of leads and customers who filled out the survey and send them a ‘thank you’ email. You could enter them into an exclusive raffle for a grand prize.

43. Referral Customers
Referrals are worth holding onto. They enter the sales funnel readier to buy thanks to the recommendation of your brand from their family, friends, or colleagues.
However, referrals need their own level of nurturing, so you should begin sending them personalized emails.
44. Affiliate Customers
Has your eCommerce business begun accruing affiliates? You should also segment these special customers into a separate group so you can continue nurturing these relationships with targeted email campaigns.
45. Email Domain Type
Email domains include virtual aliases, virtual mailboxes, local domains, or business domains. Using this as a criterion for segmentation reduces instances of your emails getting caught in the spam filter.
46. Desktop vs Mobile Usage
You can expect your audience to predominantly reach you on mobile devices like a smartphone or tablet, but users who find you via desktop are still out there. Optimize both experiences but also use this sticking point to segment your eCommerce audience.
47. Purchase Behavior Changes
Have you noticed changes in how your customers purchase your products or services? Perhaps they’ve abruptly stopped, or maybe you’ve had the opposite issue, and your customers are buying more from you than ever.
Flag the customers with abnormal purchasing behavior based on what you’ve observed as the average, and use email marketing to alter their purchasing behavior.
48. Engagement Changes
You should also set aside the contacts on your email list who are less engaged. Create a separate list for the customers who seem on the cusp of too much engagement. Curtail your emails to the latter group.
Don’t necessarily increase the frequency of emails to a less engaged audience but try different types of emails to engage them. Consider sending them a discount code to push them toward a purchasing decision.
Read also: Unmasking Your Audience: The Power of Customer Demographics
49. Customer Satisfaction
Happy customers make the world go ‘round. Behavior segmentation based on customer satisfaction levels allows your eCommerce business to remediate customer service for the less pleased customers and maintain it for the customers that look forward to your content.
50. Abandoned Form Status
Did leads fill out an initial form only to cease further interaction with your business? Introduce a list based on form status. You can send a reminder email to these leads to engage with them early.
51. Inactivity
You should also segment your audience based on inactive leads and customers. A low open and click-through rate among this audience subset paints a dire picture. The customers might soon unsubscribe.
Sending targeted emails designed to reengage this segment can prevent your small business from losing these customers.
Read also: Predictive Analytics for eCommerce Emails: Beginner’s Guide
Bottom Line
Email list segmentation helps you build targeted eCommerce email marketing campaigns that speak to your audience’s pain points, interests, and budget.
We hope that you’re ready to begin sending tailored, personalized content to increase your email performance and customer satisfaction.
To try marketing automation and CRM software (all-in-one) for free, sign up for EngageBay today.
